Learn About the Raid Levels in detail
RAID Levels
RAID is a storage technology that combines multiple disk drive components into a logical unit for the purposes of data redundancy and performance improvement. Data is distributed across the drives in one of several ways, referred to as RAID levels, depending on the specific level of redundancy and performance required.

There are two types of RAID:
Hardware RAID
Advantages and disadvantages with hardware-based RAID. It's more expensive, because configuring it requires an additional hardware component, a RAID controller which is a piece of hardware that controls the RAID array. Hardware- based RAID is also considered a better performing, more efficient way to implement RAID than software RAID. Hardware-based RAID is used most in corporate servers and business-class NAS drives.
Software RAID
Software RAID is arguably not as reliable as hardware RAID, but it's definitely more economical and can still deliver basic fault tolerance. You can't configure RAID arrays as complex with software as you can with hardware, but if you just want to implement mirroring (which is copying data from one drive to another, to keep that data accessible in case a drive fails) then software RAID is a cheaper, less complicated to set up option. Instead of using a bunch of disks and a controller to make an array, some software RAID solutions can use logical partitions on a single disk. That's what makes it both cheaper and less reliable if that single disk fails completely, your data is gone.
What level/type of RAID Is Right For Me?
Once you've decided whether software or hardware RAID best suits your purposes, you need to pick a RAID level this refers to how you are going to configure RAID on your device. There are several RAID levels, and the one you choose depends on whether you are using RAID for performance or fault tolerance (or both). It also matters whether you have hardware or software RAID, because software supports fewer levels than hardware-based RAID. In the case of hardware RAID, the type of controller you have matters, too. Different controllers support different levels of RAID and also dictate the kinds of disks you can use in an array: SAS, SATA or SSD).
List of RAID Levels:
To learn more about each RAID LEVEL just click on their links.
RAID LEVEL 0
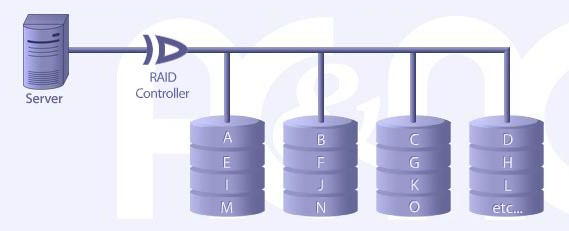
Raid Level 0
RAID LEVEL 1
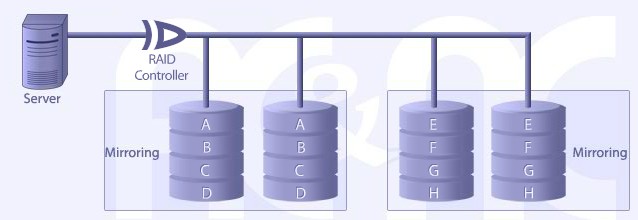
Raid Level 1
RAID LEVEL 2
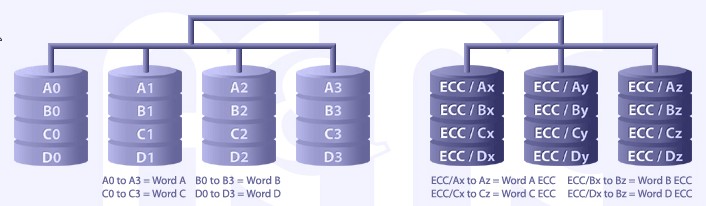
Raid Level 2
RAID LEVEL 3
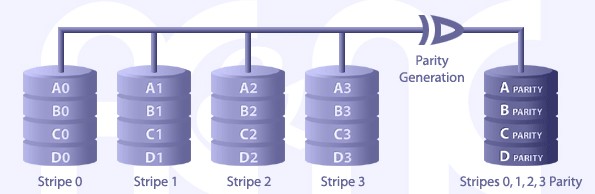
Raid Level 3
RAID LEVEL 4
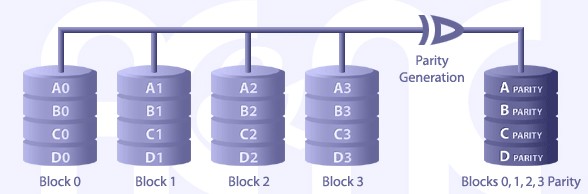
Raid Level 4
RAID LEVEL 5
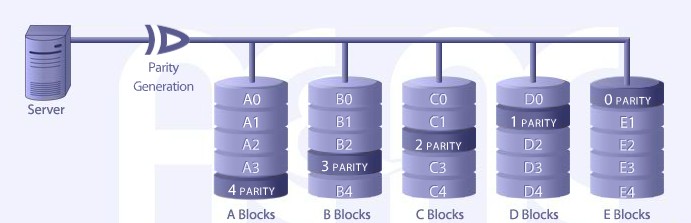
Raid Level 5
RAID LEVEL 6
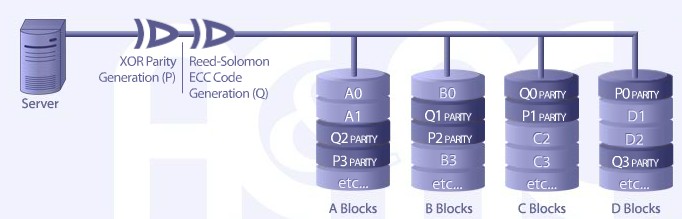
Raid Level 6
RAID LEVEL 10
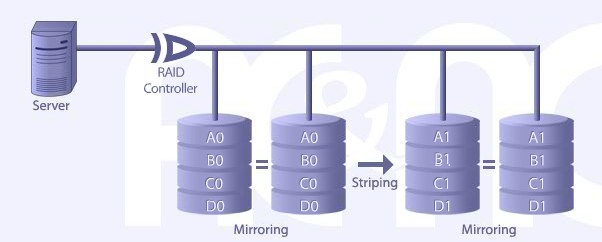
Raid Level 10
RAID LEVEL 50
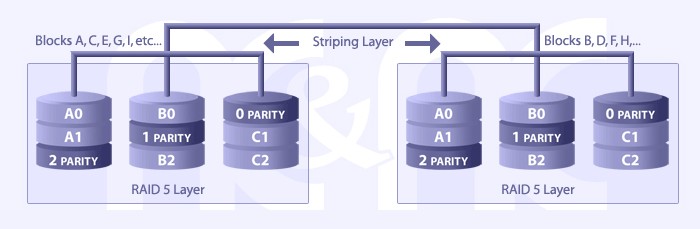
Raid Level 50
To learn more about each RAID LEVEL just click on their links.

 Raid Level 0
Raid Level 0
 Raid Level 1
Raid Level 1
 Raid Level 2
Raid Level 2
 Raid Level 3
Raid Level 3
 Raid Level 4
Raid Level 4
 Raid Level 5
Raid Level 5
 Raid Level 6
Raid Level 6
 Raid Level 10
Raid Level 10
 Raid Level 50
To learn more about each RAID LEVEL just click on their links.
Raid Level 50
To learn more about each RAID LEVEL just click on their links.
